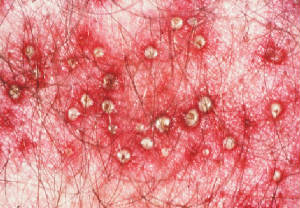
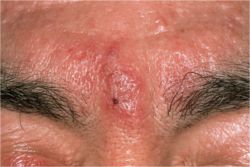
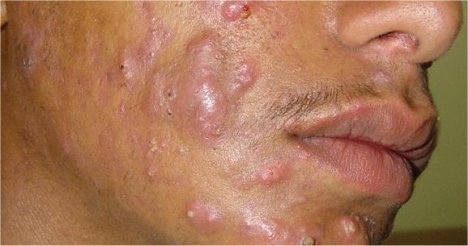
Nodulocystic acne is also known as Cystic acne, it is a severe form of acne wherein acne develops into small cysts. Acne cysts are not true cysts in the sense that they are not abnormal dilations of skin structure, but rather nodules of inflammation. Although not uncommon, it is rarer than other types of acne. Like other forms, it is caused by an excess buildup of sebum in the pores and, contrary to popular belief, is not caused by, nor is it affected by, hygiene or the lack thereof. A common treatment for cystic acne is isotretinoin, which cures most acne in about 90% of patients.
Cystic acne can affect the face, chest, back, shoulders and, occasionally, upper arms. Like pimples, which are more common, cysts are usually filled with a white pus-like substance. They are usually several millimeters in diameter, and can be quite painful.
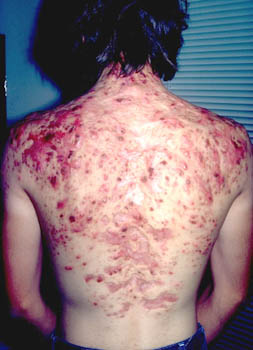
If cystic acne is not treated early on, especially with antibiotics along with a topical cream, some degree of scarring will occur.

This can be quite severe depending on the case. Although many scars can be treated, scars on the body often do not respond as well as those on the face. In most cases, it is unlikely that all scars can be removed.
Filed under: . Acne cysts, isotretinoin, pimples, scarring | Tagged: Cystic acne, Nodulocystic acne | Leave a comment »